In the early years of the 18th and 19th centuries it was fashionable, for wealthy British families, to send their son and heir on a tour of Europe. A trip that was designed to introduce the young ‘milord‘ to the art, history and culture of Italy. The British educational system was based on Latin and Greek literature and philosophy. An educated person was taught the classics from a very early age. Whilst the original Grand Tourists were mostly male, there were a few enlightened families who sent their daughters to ‘the continent’ too. Aristocratic families regarded this journey to Europe as an opportunity to complete their education. The journey was known as the ‘Grand Tour’. The young gentlemen and a few ladies were often accompanied by a ‘learned guide’ a person who could act as a tutor and chaperone. These guides, usually highly educated, were known in Italian as ‘cicerone’ and it was their job to explain the history, art and literature of Italy to their young charges.
A ‘Grand Tour’ generally included visits to Rome, Naples, Venice and Florence. On the journey south Geneva or Montreux in Switzerland were popular stopping off points too. Think Daisy Miller in Henry James novella of the same name. Wealthy families traversed Europe, often for months on end, absorbing every possible palace, party and picnic in the process. For many it was a very long and decadent party for others it was a necessary departure from their homeland until the dust of a divorce, bankruptcy or other social scandal had settled.
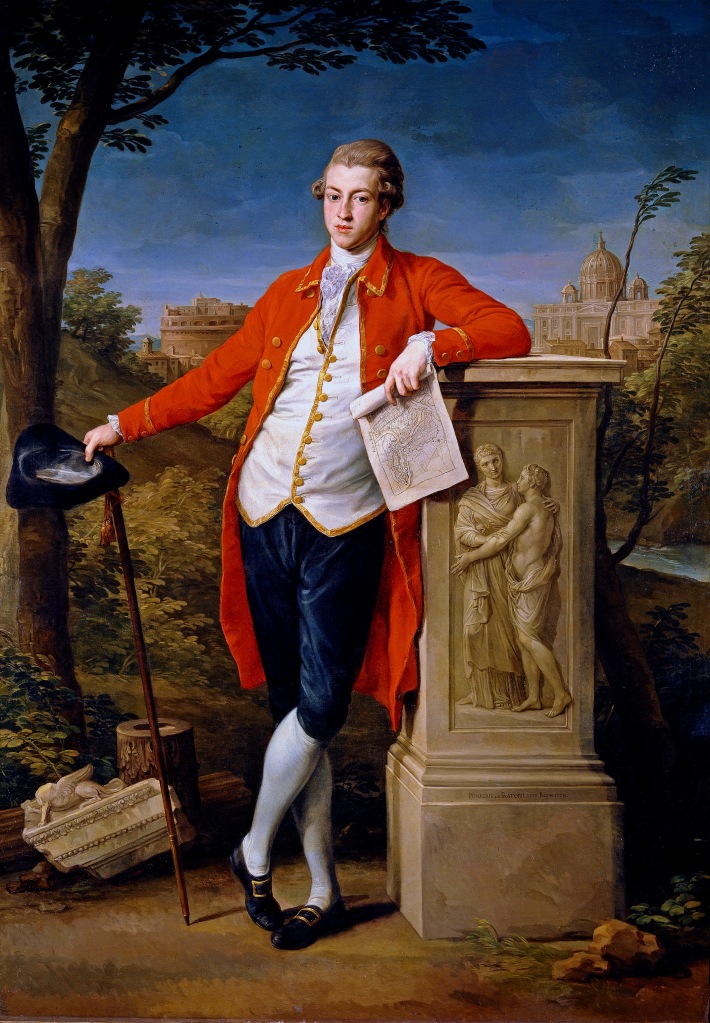

THE JOURNEY – Young gentlemen would make the journey south from The British Isles, either by ship or overland by horse and carriage. There are numerous reports of these young travellers being made chronically ill by travel sickness, rough seas and ‘foreign food’. In the 1730s and 1740s roads were rough and full of potholes, carriages could expect to cover a maximum of 15-20 miles per day. Highwaymen and groups of brigands often preyed on travellers, hoping to steal money and jewels. In the days of the ‘Grand Tour’ travel wasn’t for the faint-hearted. Crossing the Alps was a particular challenge. Depending on the age and level of fitness of travellers, it may have been necessary to hire a sedan chair to be carried, literally, by strong local men over various Alpine passes. In fact the ‘chairmen of Mont Cenis’ close to Val d’Isere were known throughout the Alps for their strength and dexterity. These ‘chair carriers’ worked in pairs and groups of four, six or even eight men – they physically carried the ‘Grand Tourists’ over the Alps.
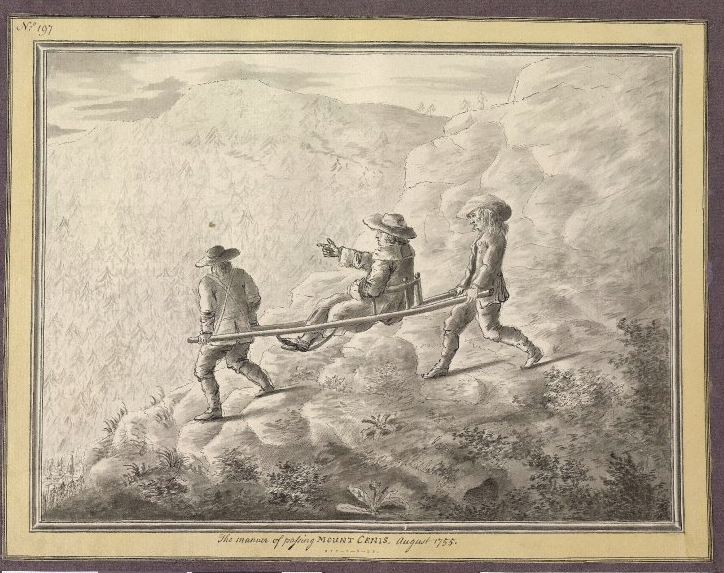

- Grand Tourist carried over The Alps in a sedan chair. The chairmen of Mont Cenis were regarded as the best, strong and agile! 1755 – George Keate
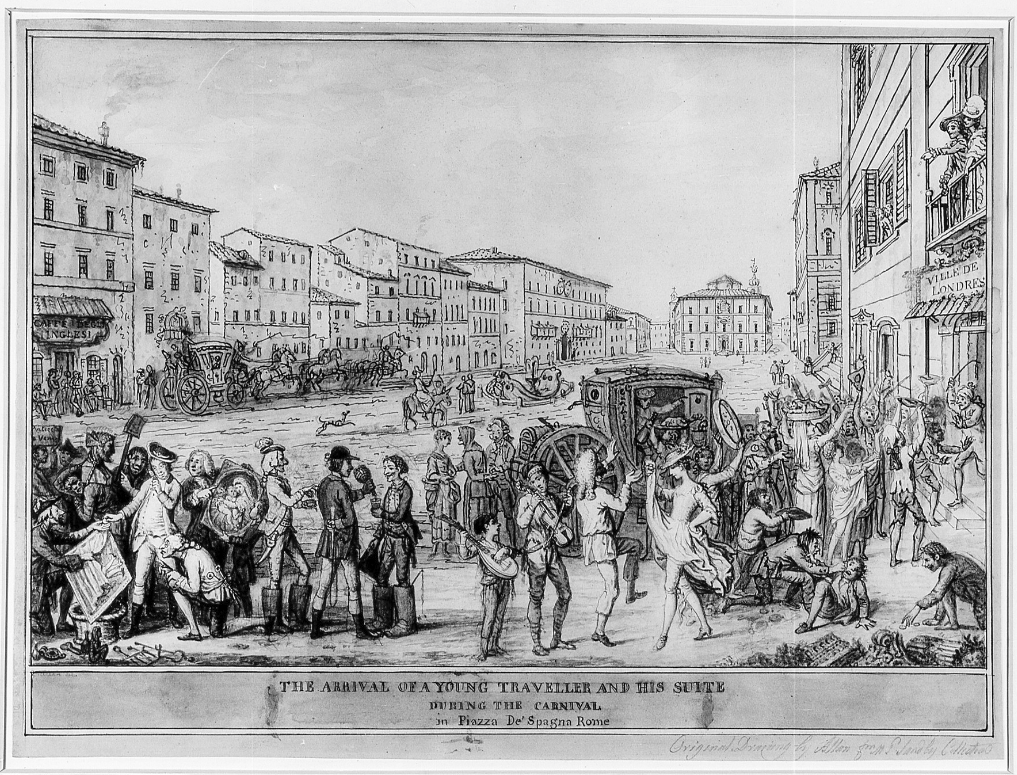



TRAVELLING – Having endured a crossing of the Alps the young ‘milordi’ would head to Milan or Turin where the local British consulate would offer a warm welcome. However, the really attractive destinations were further away, particularly Venice, Florence, Rome and Naples. These cities were renowned for their entertainment, lavish parties and sense of fun. There’s a fantastic cartoon, by David Allen (above) showing a young aristocrat arriving in Piazza di Spagna, Rome. His carriage is instantly surrounded by local touts, street performers, actors and actresses, all anxious to separate young ‘Algernon’ from his trunk full of cash! It’s interesting to remember that the Italians have been welcoming tourists to their lands for centuries. They’ve learned a thing or two about helping newly arrived foreigners!
VENICE – In Venice the British Consul Joseph Smith was an art collector and supporter of local artists. Smith lived in a small palace on the Grand Canal, filled with paintings, art, books and coins. He was patron of Canaletto, probably the most famous and popular Venetian painter of his day. Canaletto painted ‘vedute’ scenes of Venice. Every Grand Tourist wanted to leave with a Canaletto painting as a souvenir of the Grand Tour. Smith’s art collection was so impressive that a young King George III purchased the entire collection in 1762, when he was himself on the Grand Tour. So Joseph Smith’s art collection became the basis of the British ‘Royal Collection’ of art much of which can still be seen at Buckingham Palace or in the National Gallery, London today. Whilst in Venice the young Grand Tourists would attend concerts, visit churches and wherever possible attend a ball or two. Venice at Carnival time was a particular fascination – an opportunity to put on a mask and be whoever you wanted to be!
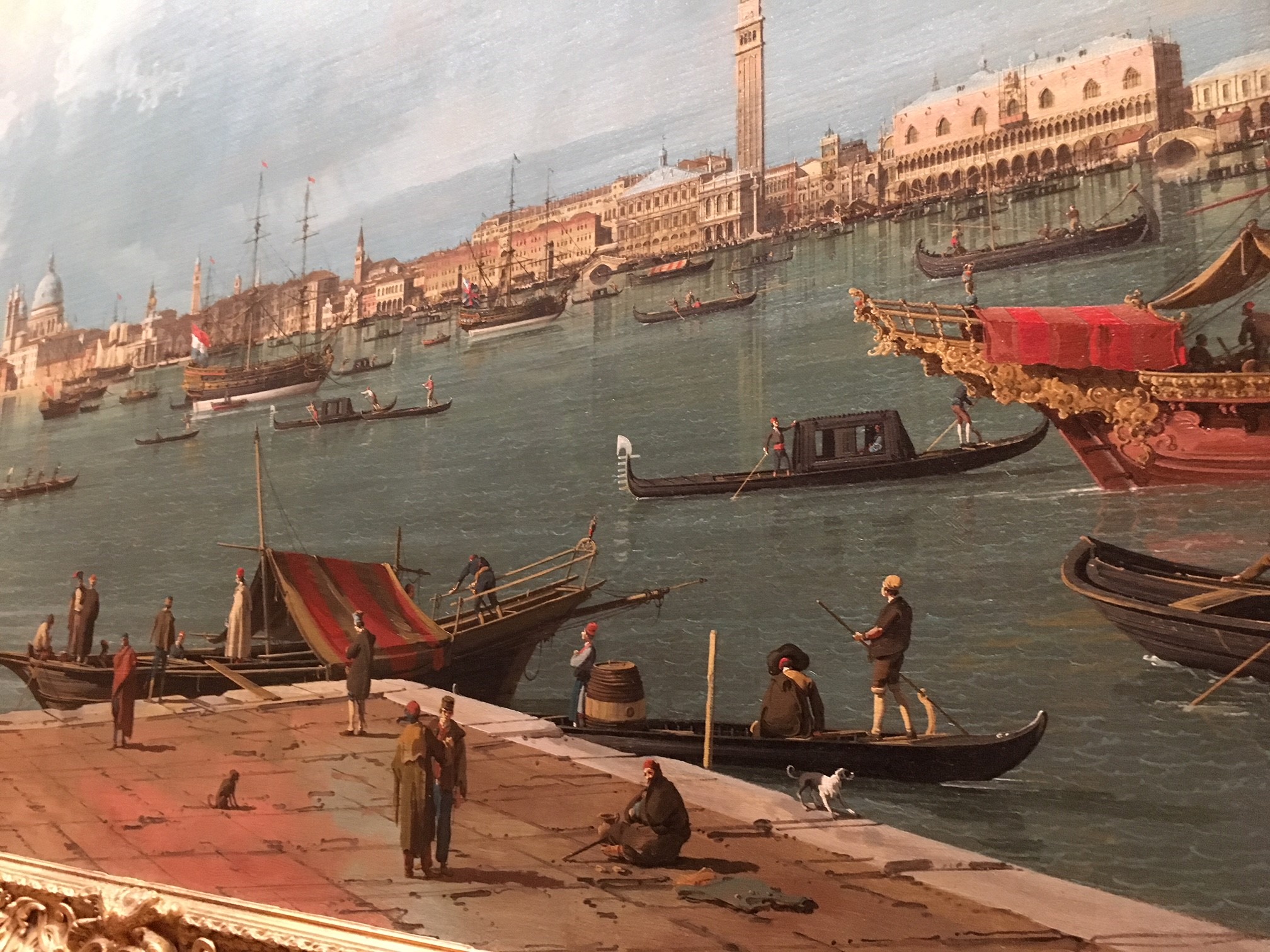
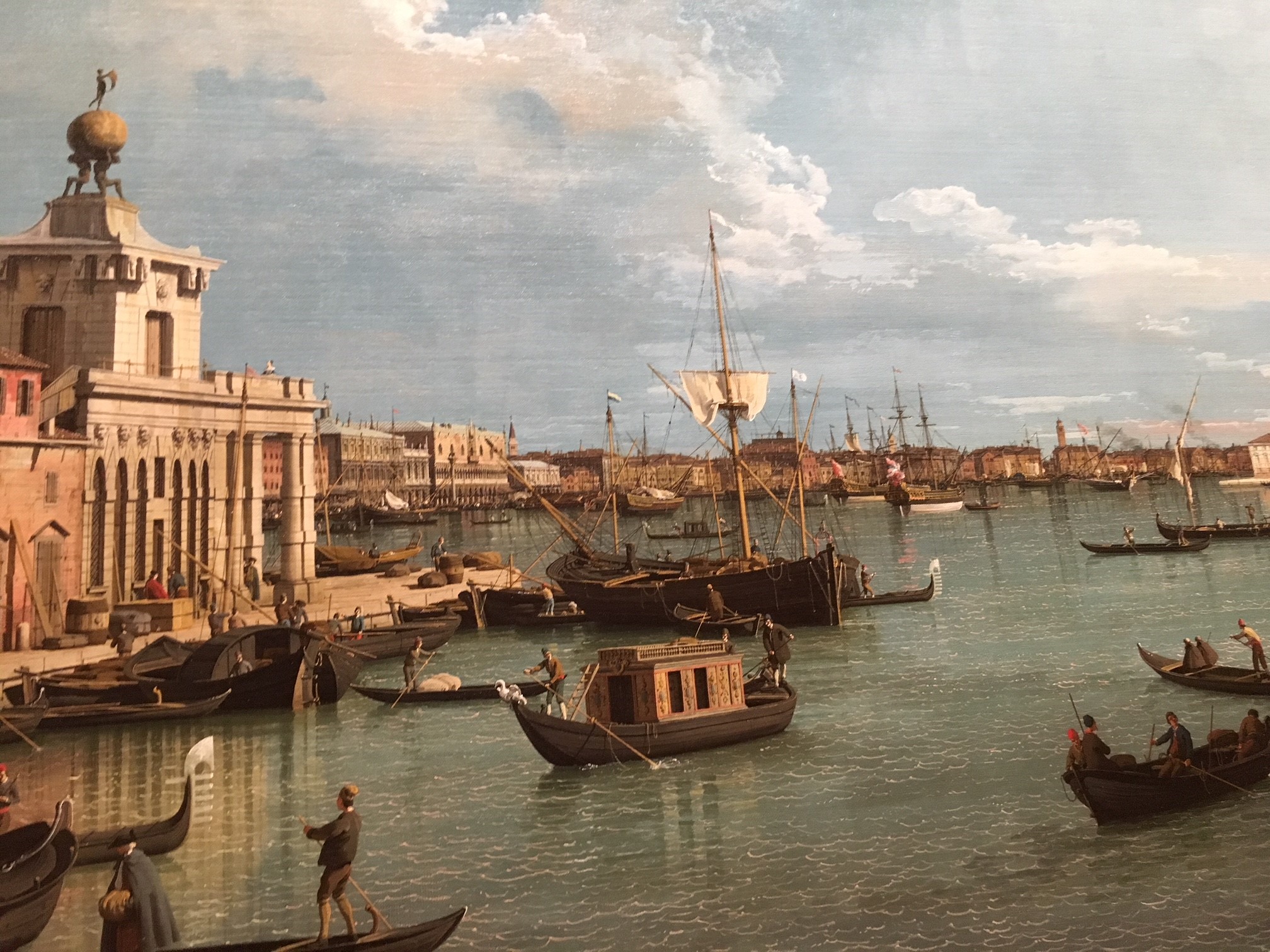
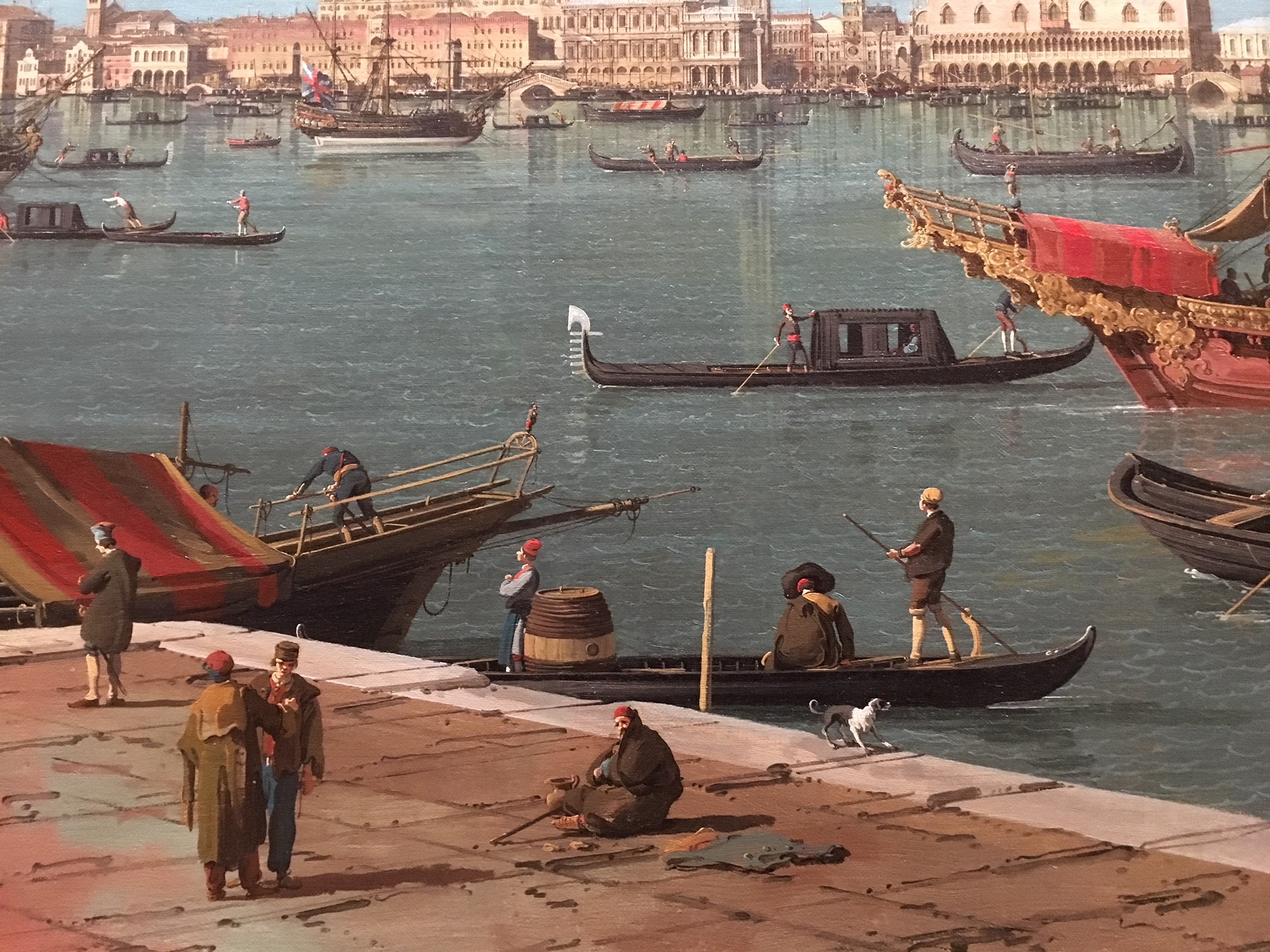



A typical Grand Tour of Europe could last up to two years and would always include several months staying in each city visited.

Florence was popular for its renaissance art, magnificent country villas and gardens, whilst Rome was essential for proper, classical, ancient ruins. Venice was the party city, especially at the time of Carnival. Naples was regarded as the home of archaeology, excavations at Pompeii and Herculaneum began in the 1730s and Vesuvius was quite active at this time. Plumes of volcanic gases and occasional lava flows would illuminate the mountain after dark. The Grand Tourists would position themselves on the lower slopes of the volcano to watch the nightly spectacle.
IN ROME – many of the Grand Tourists funded excavation work in and around the Roman Forum and the Colosseum. Many of the Grand Tourists wanted to acquire a Roman statue or sculpture to take home as a souvenir. There were numerous stonemasons working in and around the basement of the Colosseum, creating modern and ‘antique’ marble sculptures. Even in the 18th century demand exceeded supply in the ‘genuine Roman sculpture market’. Many Grand Tourists left for home with an ‘original’ antique Roman statue, which years later, under expert examination turned out to be a fake! The artist Panini painted several imaginary compositions of young Grand Tourists surrounded by paintings of Roman buildings and ruins. Each of the ‘ruins’ in the paintings was based on an actual Roman building. For example, in the painting below The Pantheon is clearly visible just to the right of the two standing gentlemen. Above the Pantheon is the Colosseum. On the left of the painting above the two seated gentlemen the Roman arches of Constantine and Septimius Severus can be seen.
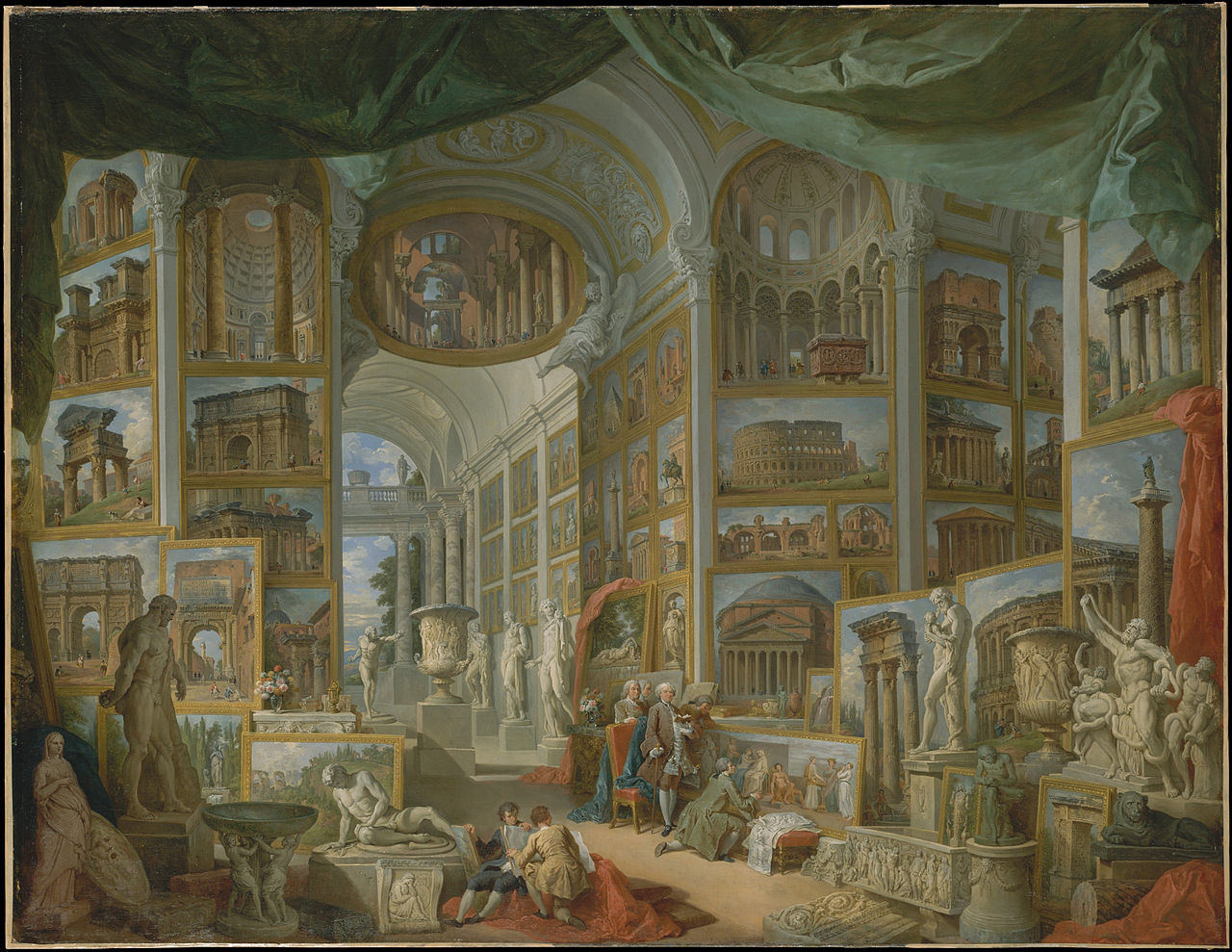

Roma Antica – by Giovanni Paolo Pannini c. 1754 – Stuttgart Art Museum
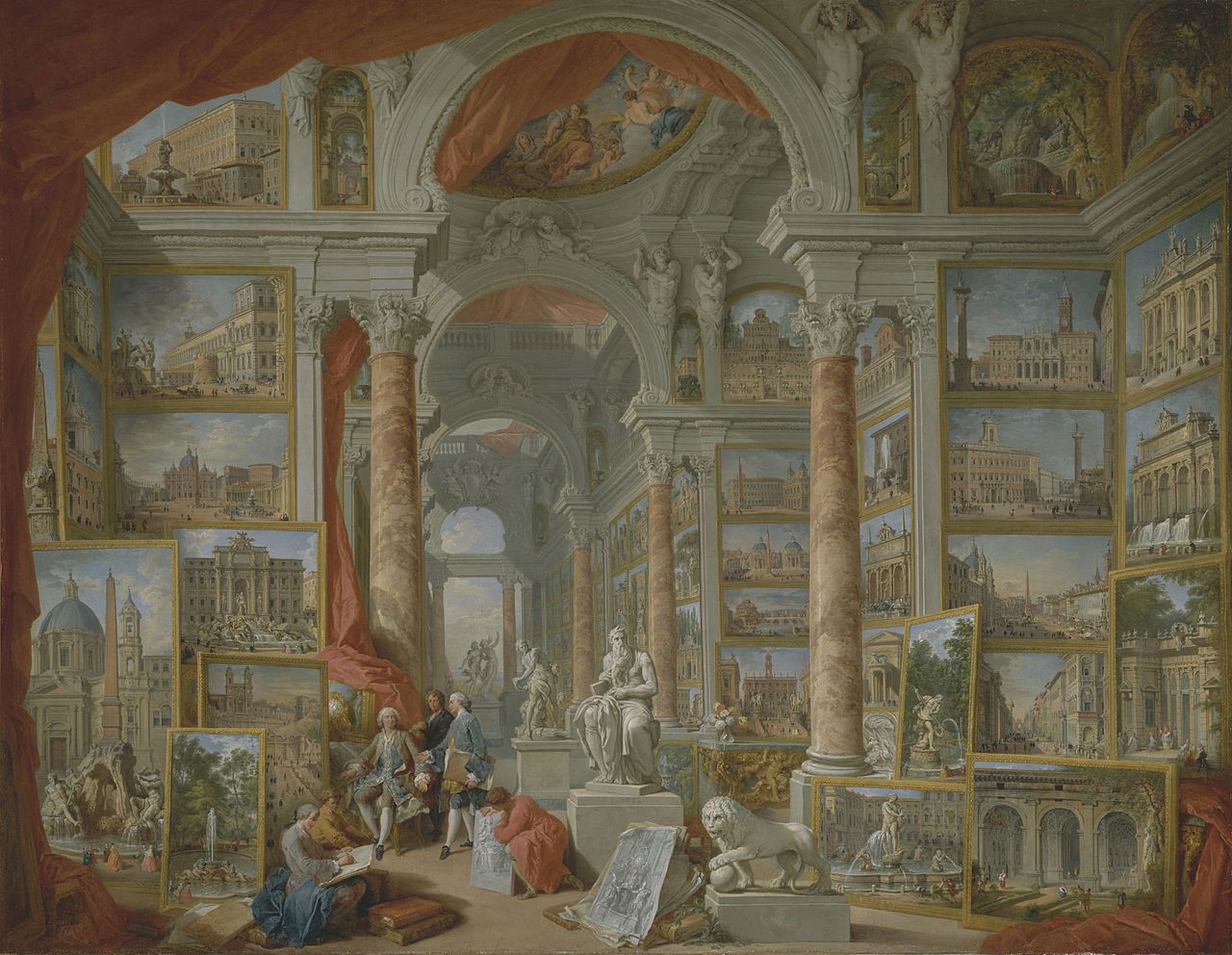
The Grand Tour inspired many travellers to take a greater interest in Roman history and art. The study of archaeology was born at this time with extensive excavations taking place in Pompeii, Herculaneum and in the area of the Roman Forum in Rome. The British School at Rome was established to learn more about the Roman ruins and to fund excavations. The School still exists today. Below is another painting by Pannini showing the wonders of Modern Rome (1750s) – featuring details of Baroque fountains, palaces and elegant piazzas. These exceptionally detailed paintings effectively catalogue the ‘ancient marbles’ discovered in Italy by the middle years of the 18th century.

NAPLES – for fun and excitement on the Grand Tour was very popular. Lord Hamilton, British Ambassador in Naples was a wonderful host and put on spectacular parties and musical evenings. His second wife Emma Hamilton would dress in Roman and Greek style clothing and perform a series of ‘Attitudes’ where guests had to guess her identity. It was here at the Hamilton residence that Emma attracted the attention of Lord Nelson, British naval hero of the day, and they became lovers.
Meanwhile Vesuvius, the volcano that dominates the Bay of Naples was having an active phase in the 1760s and 1770s, most days steam could be seen rising from the crater and frequently, especially after nightfall, streams of glowing lava could be observed. Lord Hamilton wrote several articles on Vesuvius and the lava flows that he witnessed. Many visiting painters were inspired to paint Vesuvius and the surrounding area. The science of vulcanology was in its infancy. The spectacle that Vesuvius offered visitors most nights must have seemed quite extraordinary to the early Grand Tourists – typically away from home in strange and different lands for the first time.
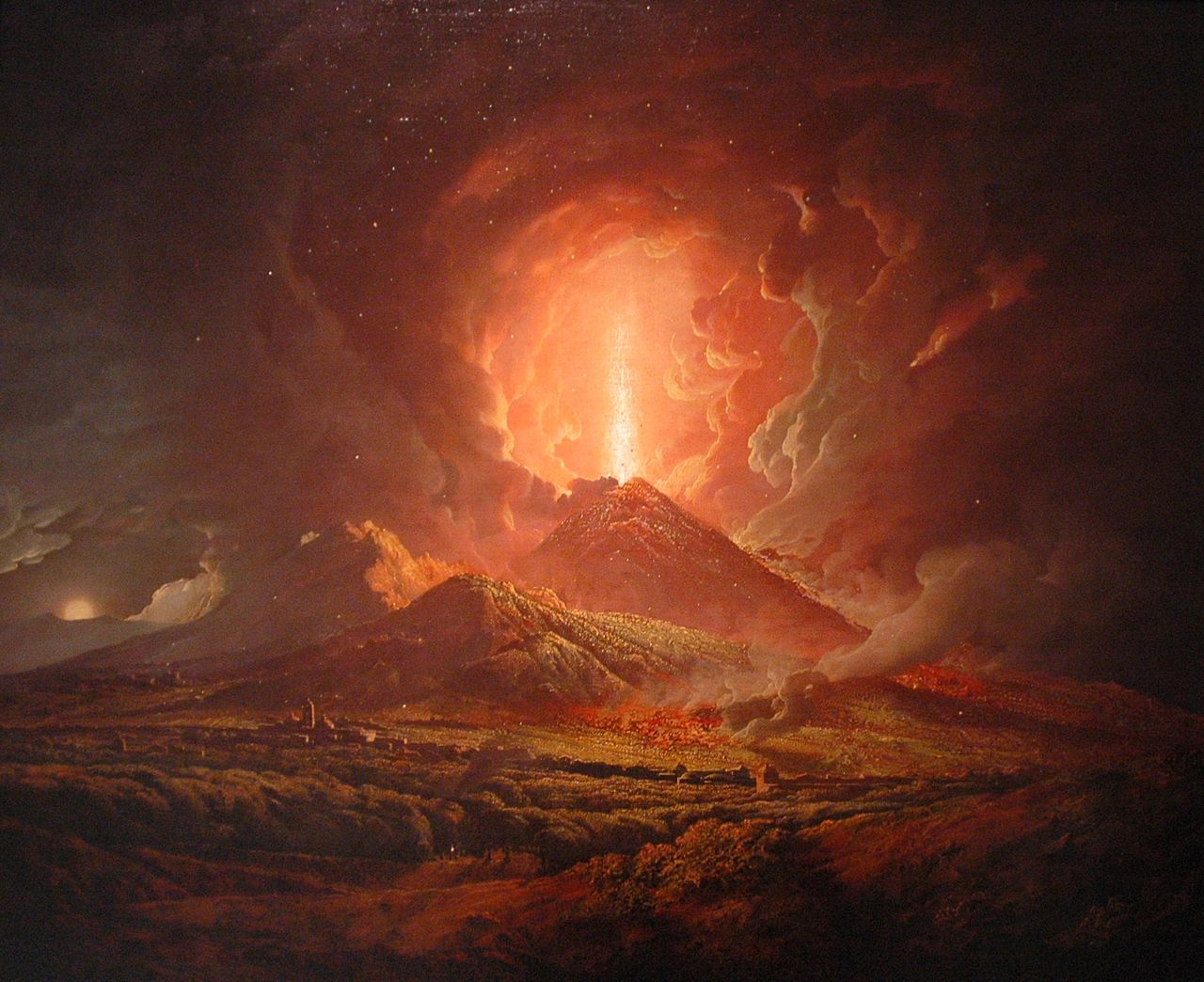
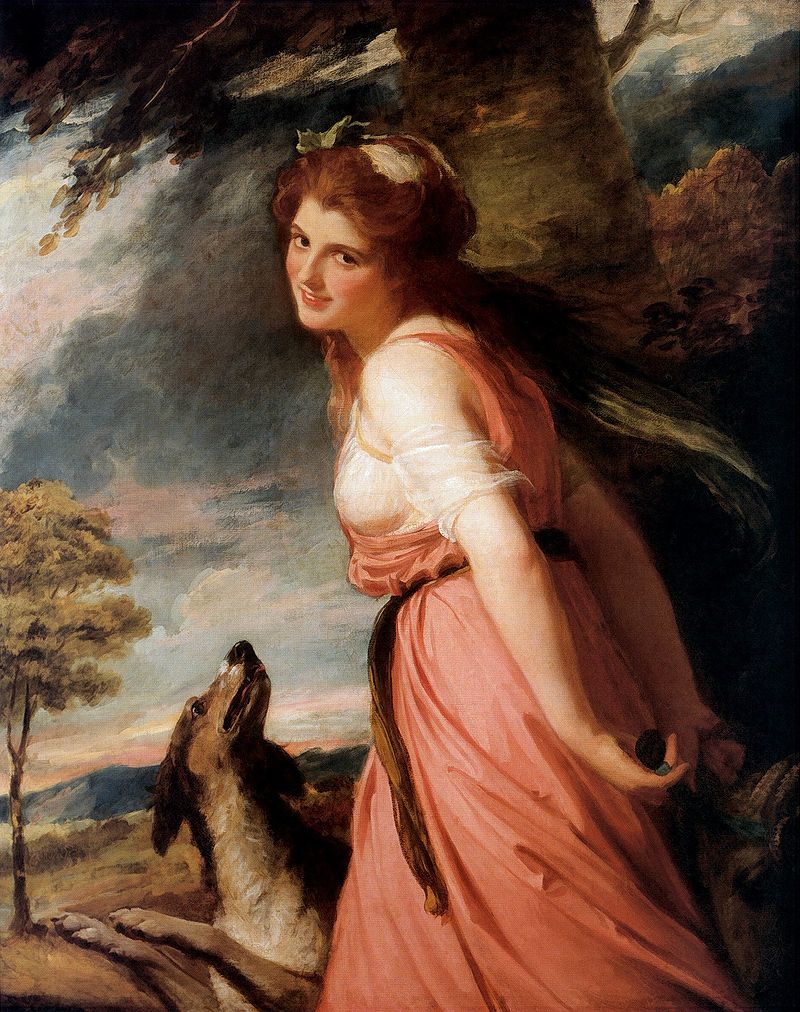
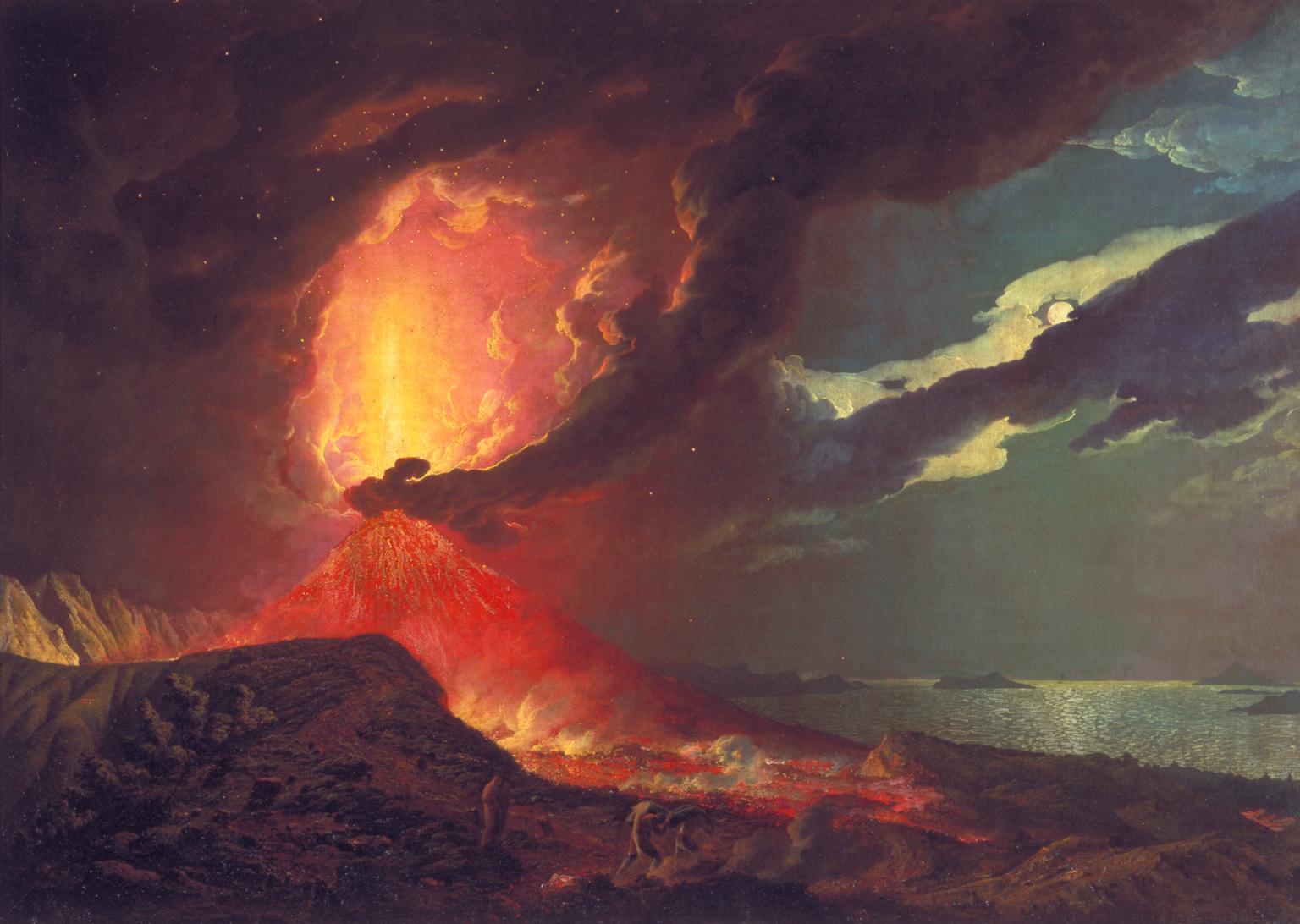
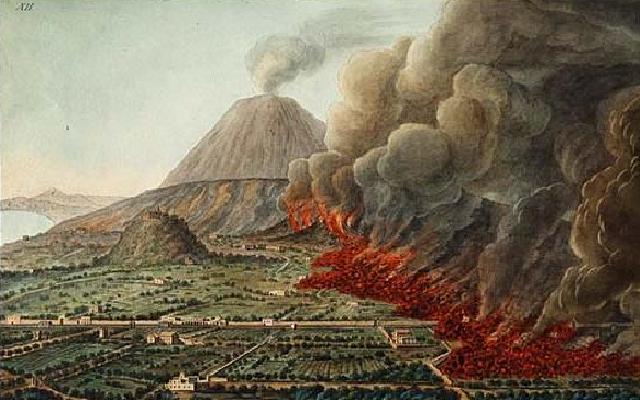




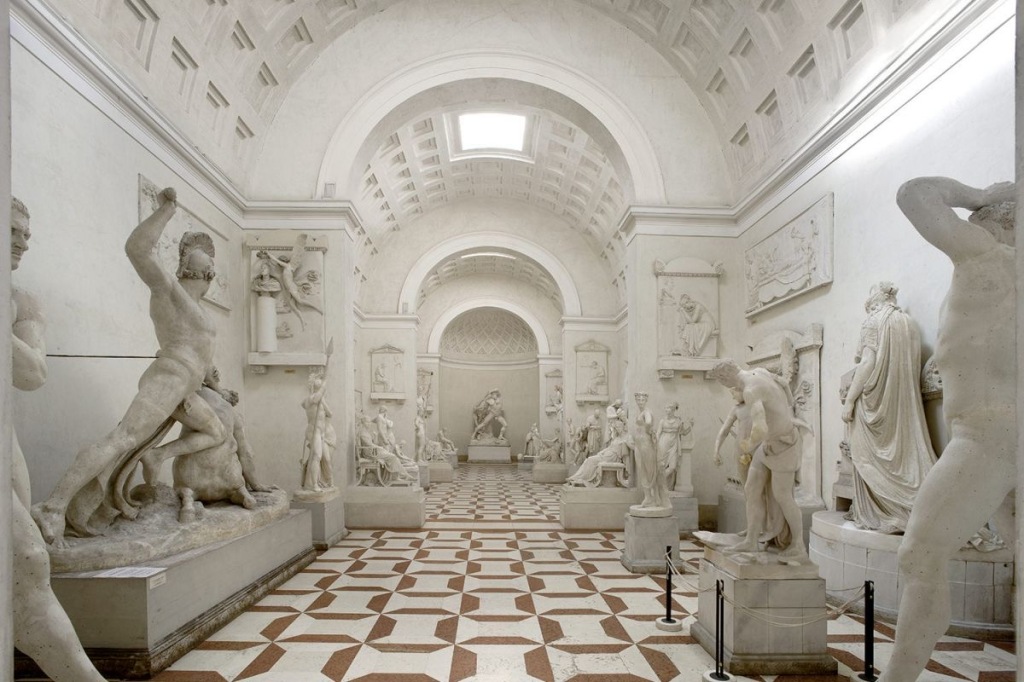
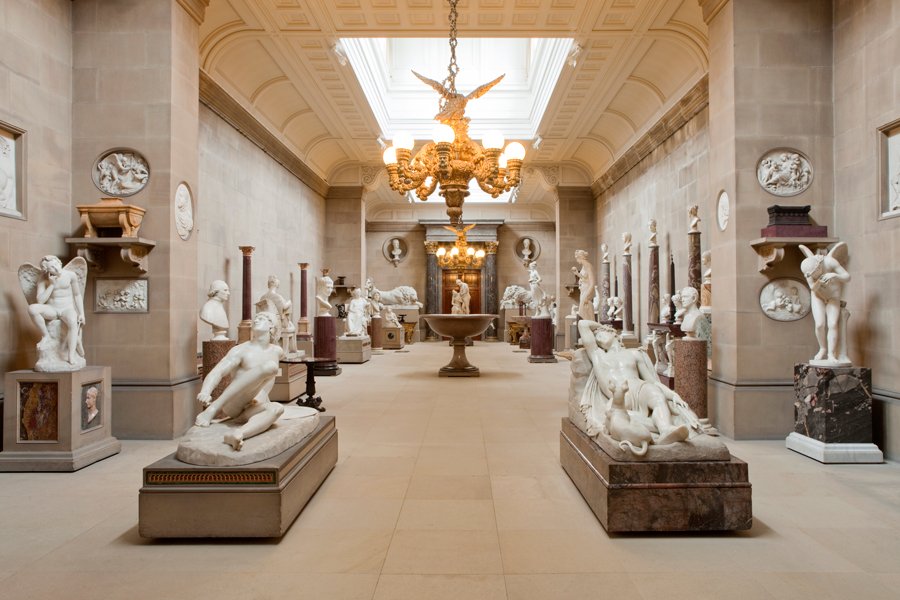
From Naples it was relatively easy to arrange transport on a British ship back to England. So Naples was a popular end point for the 18th century Grand Tour. The young aristocrats would board a ship bound for England and assuming no rough seas they’d be home within a few weeks. Typically they’d have extensive luggage including marble statues and friezes from Rome, paintings and glassware from Venice, even lava samples and pumice stone from Naples. All these souvenirs would be displayed with great pride in the family home. The impact on British country houses of the Grand Tour can still be seen today. Almost every stately home in Britain has several paintings by Canaletto, commissioned during the Grand Tour. Many stately homes have a sculpture gallery, often specially built to accommodate the Roman statues and marble work brought back from the Grand Tour.
In a sense the Grand Tour was the start of modern tourism, it was a journey taken to learn and experience new and different styles of art, architecture and culture. A journey designed to understand and learn about Europe. The Grand Tour was a couple of years enjoying the best that Europe (especially Italy) had to offer. Parties, ladies, fine food and wine – and family members at a distance – a letter from mama or papa would take weeks to arrive. The young aristocrats had freedom, fun, sun and souvenirs. What finer way to complete a young gentleman’s education. Head home with a sack full of souvenirs and a full and varied experience of life – this was escapism at its best!



Notes:
- ‘Milordi’ is a term referring to aristocratic men, literally meaning ‘my lords’. In the days of the Grand Tour the term ‘milordi’ was an ironic and satirical way of referring to young, aristocratic men, travelling in Europe with (generally speaking) more money than sense.
- Cicerone or bear-leader was a popular term for a man who escorted young men of rank or wealth on their travels on the Grand Tour. The role of cicerone or bear-leader blended elements of tutor, chaperone and companion. These tutor-companions were often hired to keep the young ‘milordi’ out of trouble and to ensure that they didn’t do anything to embarrass their families. The name Cicerone originally comes from ‘Cicero’ referring to the famous Roman orator, politician, thinker and writer., who lived from 106-43 BC.
Many of London’s museums have exceptional collections of Italian and Greek paintings and sculptures as a result of the Grand Tour. The National Gallery has an amazing collection: https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/learn-about-art/paintings-in-depth/the-grand-tour
- I’ve written about Herculaneum at the time of the eruption of Vesuvius in 79AD.
- I’ve also written other articles about Naples and Herculaneum:
- Herculaneum – a very bright future…..
- Naples, A Crazy Prince and fantastic pizza…
- To learn more about unique travel opportunities and tailor-made journeys check out our sister web site: Grand Tourist for ideas and examples of exceptional travel experiences.
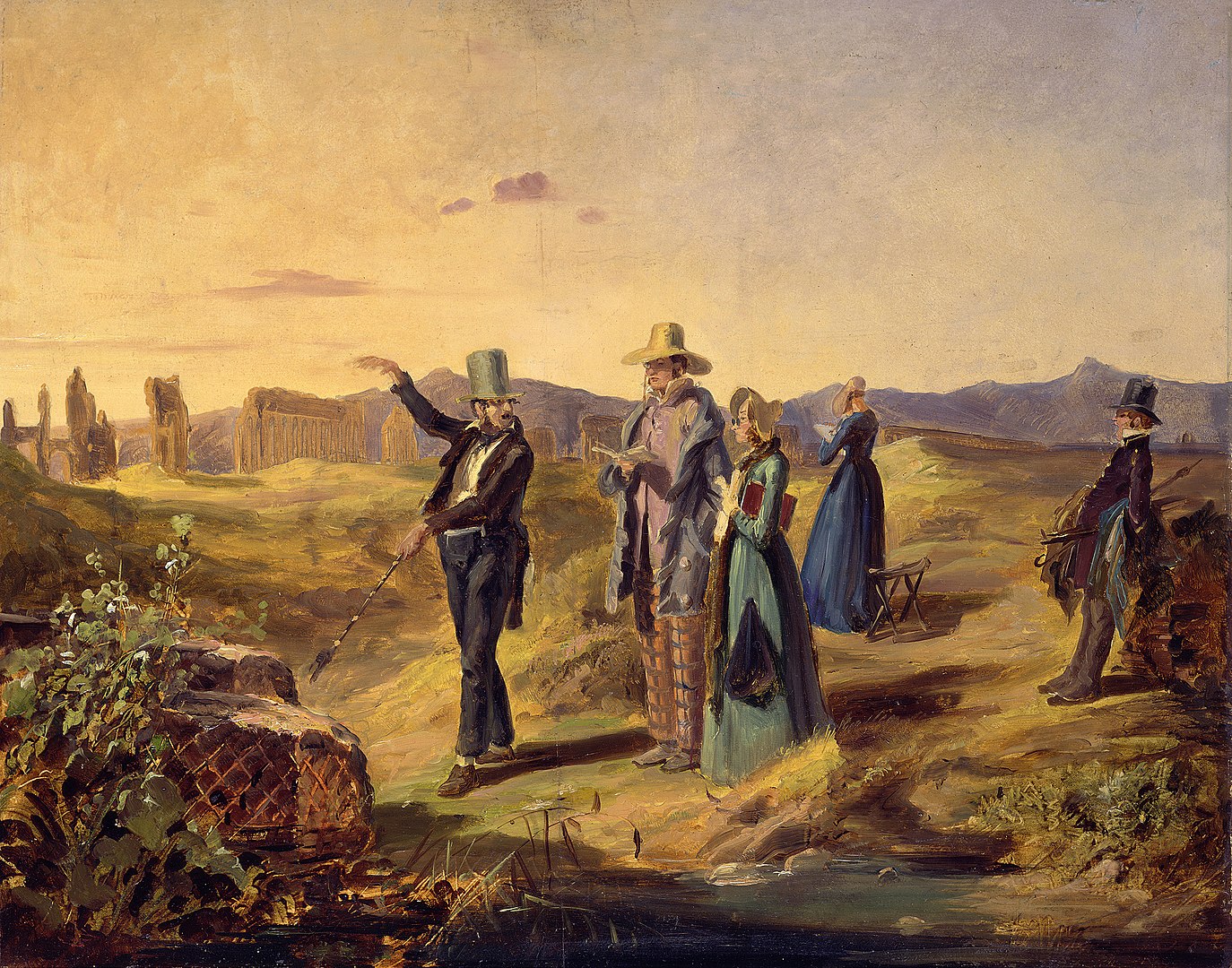
- The picture at the top of this article (reproduced below) is by German 19th century painter Carl Spitzweg. It is a wonderful, and humorous portrayal of earnest English tourists soaking in the atmosphere at a ruined temple site (it could be Paestum, south of Naples). Although I think it might be Agrigento, Sicily. The artist has captured the mood of the ‘Grand Tourists’, just look carefully at the characters!
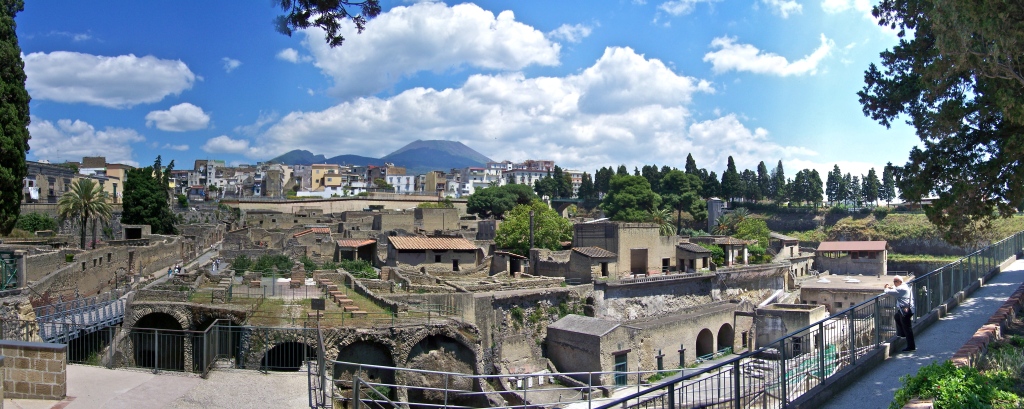





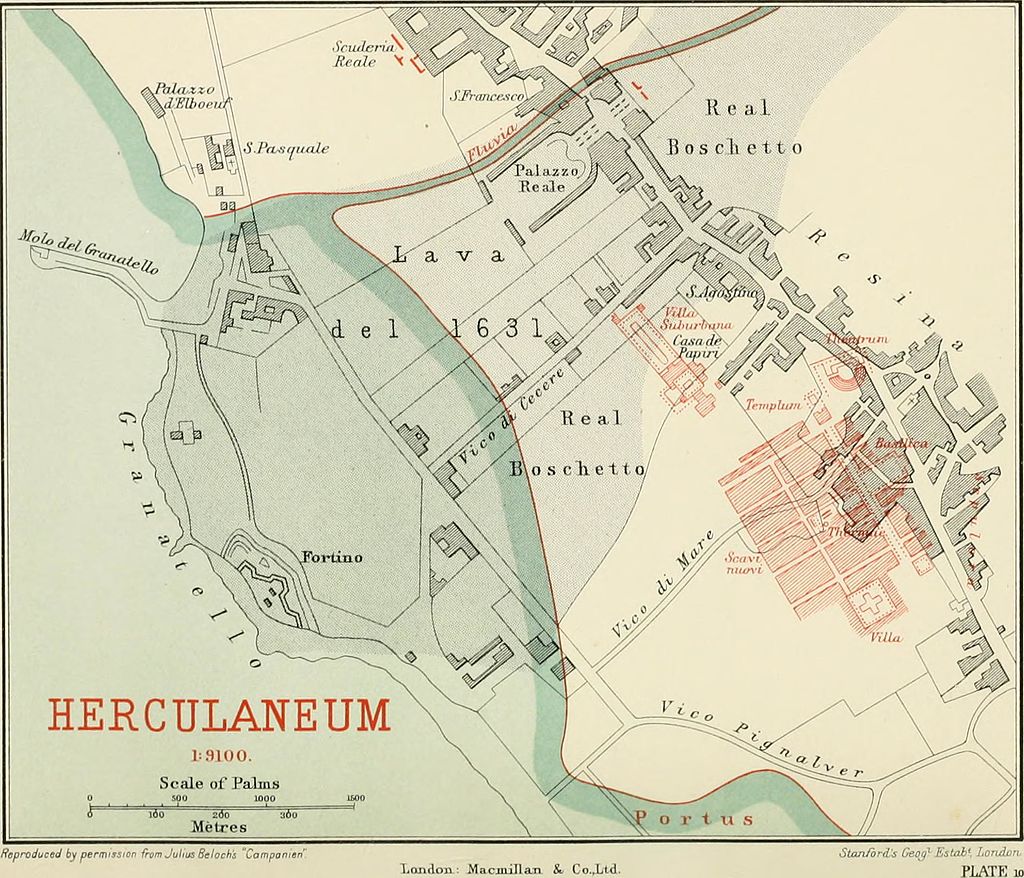
Herculaneum, Roman seaside town, buried by eruption of Vesuvius 79 AD (left). Map (right) shows areas excavated by 1908
- NOTE: Journeys in Europe are designed by our sister company www.grand-tourist.com drop us a line to discuss your perfect grand tour.
- Written: 23-11-17
- Updated: 15-11-20 / 10-01-2022 / 10-12-2023
#grandtour #grandtourist #educatedtraveller #archaeology

Thank you for including my article in your list. I am fascinated by the Grand Tour – possibly Adam Smith’s decision to leave his post and become a private tutor, meandering around Europe, was not such an unusual one. Certainly the Italian cities of Venice, Florence, Rome and Naples were filled with eager ‘tourists’ anxious to learn and often to finance restoration of ancient buildings. It must have been a very interesting time.
LikeLike
Absolutely amazing piece. Thank you for providing such interesting information!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Natalia x
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks for linking to my ‘History of the Grand Tour’. Curiously I too was an undergraduate at Oxford, although not one of the drunken ones. Were you a Rhodes or a Fulbright Scholar?
The authors who wrote for the original Grand Tourists were people like John Murray and Baedeker. In fact you couldn’t call yourself a serious ‘tourist’ without a small red volume of either writer tucked under your arm!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hello Miss Onion – thanks for finding my blog. Please can you put the source as greyhoundtrainers.com
Thank you.
Also the book about the Grand Tour is by Brian Dolan
(Katie Hickman just wrote a review)
If you want a little more background on the Grand Tour just ask – I run a travel business called Grand Tourist as well as writing my blog! Have a good day.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Excellent, enjoyably breezy summary of a very important 18th century phenomenon, really enjoyed it, thank you.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hi Arran – thank you so much for this kind comment. I’m delighted you enjoyed my summary!
LikeLike
So THIS is where the name for your tour company originated! I feel like a GRAND TOURIST when I’m traveling with you, Janet–learning as I travel just like the folks from centuries ago! Thanks for this terrific background article!
LikeLiked by 1 person
I was going to say the same as Mary Lou Peters, and congratulate you on your four bears (Darn that predictive text – I had actually dictated “congratulate you on your forebears”!) – A truly riveting and informative article – superb reading – thank you so much for that!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you John – appreciated!
LikeLike